3-HydroxyAnthranilic acid Antibody – Mouse Monoclonal
Ref: IS001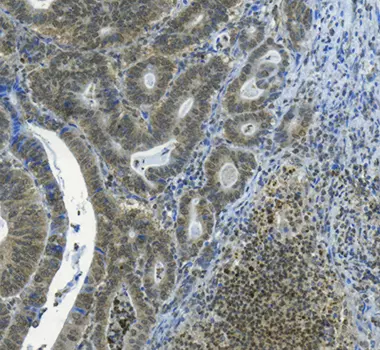 +
+IHC validation of anti-3-Hydroxy-Anthranilic acid antibody in human colon tumor
IHC staining shows accumulation of 3-hydroxy-anthranilic acid in human colon cancer cells, as well as in cells from the tumoral microenvironment. Human paraffin-embedded colon tumor tissue was subjected to pH=6 antigen retrieval, and overnight incubation with primary 3-Hydroxy-Anthranilic acid antibody (1/1000 dilution). After polymer-conjugated secondary antibody exposure, staining was observed through DAB coloration.
DatasheetMSDS
The first and only anti-3-HydroxyAnthranilic acid mouse antibody available for research use. This primary mouse monoclonal antibody was validated for IHC both in human tumor and brain tissues. When tested by competitive ELISA, the antibody demonstrated strong affinity and high specificity.
| Clonality | Monoclonal antibody (clone 5B2-G2) |
| Host | Mouse |
| Valided applications | IHC |
| Reactivity | Reacts with all species |
| Format | 50µL |
| References | Cited in 3 papers |
Product overview
| Product name | 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid antibody |
| Synonyms | Anti-3-Hydroxy-Anthranilic acid antibody
2-Amino-3-hydroxybenzoic acid antibody 3-OH-Anthranilic acid antibody 3-hydroxanthranilate antibody 3-OHAA antibody |
| Immunogen | Conjugated 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid |
| Isotype | IgG1 k chain |
| Clone | Clone 5B2-G2 |
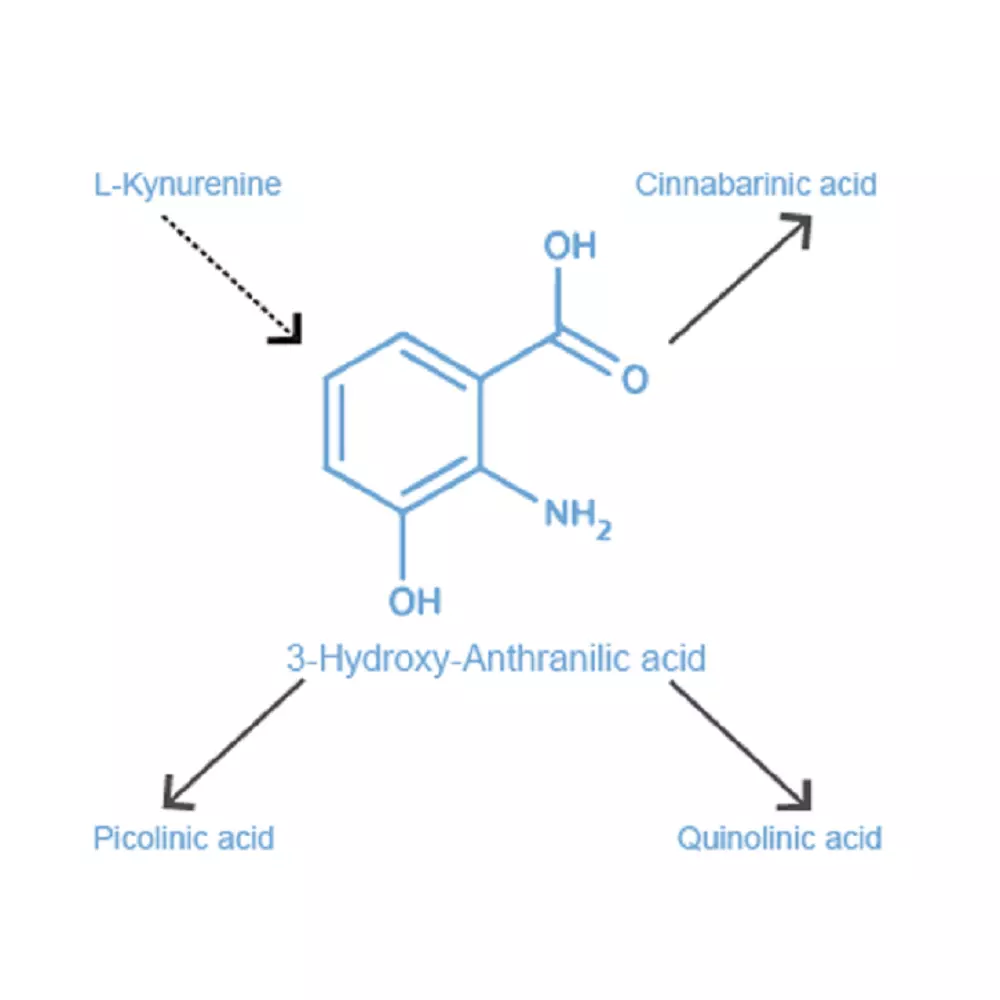
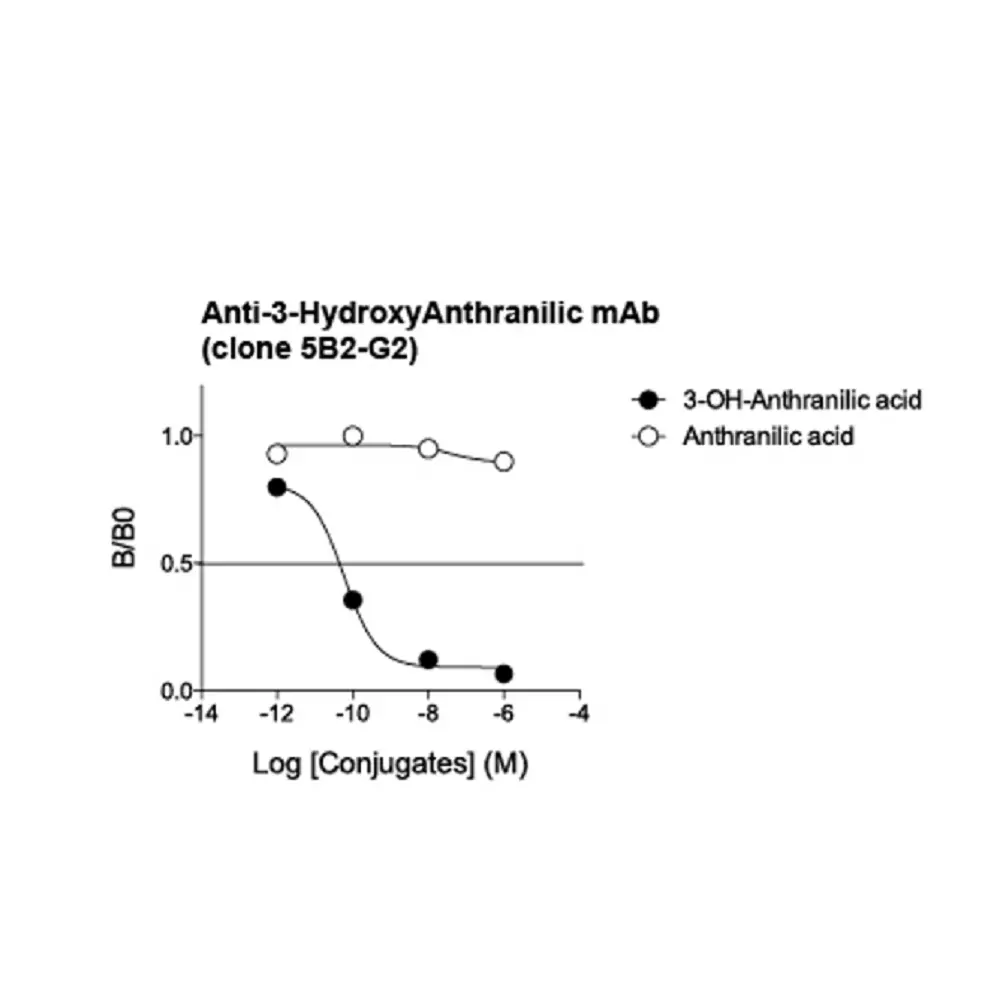
| Specificity | When tested in competitive ELISA, the anti- 3-HydroxyAnthranilic acid antibody did not show any significant cross reactivity with Anthranilic acid or Cinnabarinic acid conjugates |
Storage
| Form | Liquid |
| Purity | Purified IgG |
| Concentration | 0,5 mg/ml |
| Storage |
Store at +4°C for short term (1-2 months). Aliquot and store at -20°C for long term. Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles |
| Material safety datasheet | Download MSDS |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | Dilute at 1:200-1:2000. Perform heat antigen retrieval (pH=6) before initiating IHC staining protocol on paraffin-embedded and frozen sections |
| Immunofluorescence (IF) | Dilute at 1:100-1:1000 on paraffin-embedded and frozen sections. Perform heat antigen retrieval and incubate with fluorescent dyes conjugated secondary antibody |
| Comments | Optimal working dilutions must be determined by the end-user |
| Restrictions | For research use only |
Product citation
- 3-Hydroxyanthranic acid inhibits growth of oral squamous carcinoma cells through growth arrest and DNA damage inducible alpha
Check article
Authors : Gan et al., Transl Oncol.
2025-01 - Marked IDO2 expression and activity related to autophagy and apoptosis in brain tissue of fatal tuberculous meningitis
Check article
Authors : Guo et al., Tuberculosis
2024-02 - Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-1 and IDO-2 activity and severe course of COVID-19
Check the article
Authors : Guo et al., Journal of Pathology
2022-01